
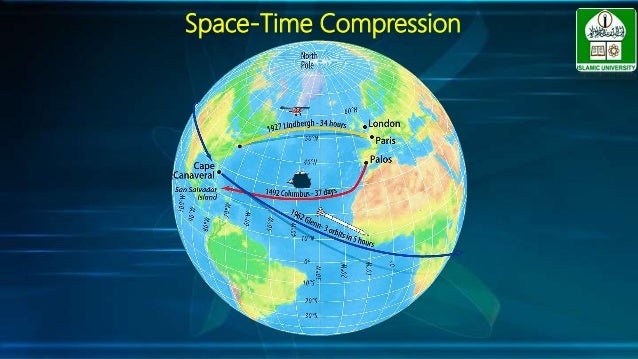
But if it does turn out that a new theory of gravity is needed, what kind of theory would it be? How could it correctly describe the motion of the bodies in the Solar System, as Einstein's theory is known to do, and still give us the different prediction for the universe that we need? There are candidate theories, but none are compelling. This fact would provide a way to decide if the solution to the dark energy problem is a new gravity theory or not: we could observe how galaxies come together in clusters. That would not only affect the expansion of the universe, but it would also affect the way that normal matter in galaxies and clusters of galaxies behaved. So the mystery continues.Ī last possibility is that Einstein's theory of gravity is not correct. But, if quintessence is the answer, we still don't know what it is like, what it interacts with, or why it exists. Some theorists have named this "quintessence," after the fifth element of the Greek philosophers. So the mystery continues.Īnother explanation for dark energy is that it is a new kind of dynamical energy fluid or field, something that fills all of space but something whose effect on the expansion of the universe is the opposite of that of matter and normal energy. The number came out 10 120 times too big. But when physicists tried to calculate how much energy this would give empty space, the answer came out wrong - wrong by a lot.
SPACE IN TIME DEFINITION FULL
In this theory, "empty space" is actually full of temporary ("virtual") particles that continually form and then disappear. The result could present a challenge to basic theories of dark matter.Īnother explanation for how space acquires energy comes from the quantum theory of matter. This image shows the distribution of dark matter, galaxies, and hot gas in the core of the merging galaxy cluster Abell 520. Come to think of it, maybe it shouldn't be called "normal" matter at all, since it is such a small fraction of the universe. The rest - everything on Earth, everything ever observed with all of our instruments, all normal matter - adds up to less than 5% of the universe. It turns out that roughly 68% of the universe is dark energy. Other than that, it is a complete mystery. We know how much dark energy there is because we know how it affects the universe's expansion.
Theorists still don't know what the correct explanation is, but they have given the solution a name. Maybe there is something wrong with Einstein's theory of gravity and a new theory could include some kind of field that creates this cosmic acceleration. Maybe it was a result of a long-discarded version of Einstein's theory of gravity, one that contained what was called a "cosmological constant." Maybe there was some strange kind of energy-fluid that filled space. But something was causing it.Įventually theorists came up with three sorts of explanations.
SPACE IN TIME DEFINITION HOW TO
No one expected this, no one knew how to explain it. So the expansion of the universe has not been slowing due to gravity, as everyone thought, it has been accelerating. Then came 1998 and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) observations of very distant supernovae that showed that, a long time ago, the universe was actually expanding more slowly than it is today. The universe is full of matter and the attractive force of gravity pulls all matter together. Granted, the slowing had not been observed, but, theoretically, the universe had to slow. It might have enough energy density to stop its expansion and recollapse, it might have so little energy density that it would never stop expanding, but gravity was certain to slow the expansion as time went on. In the early 1990s, one thing was fairly certain about the expansion of the universe.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
